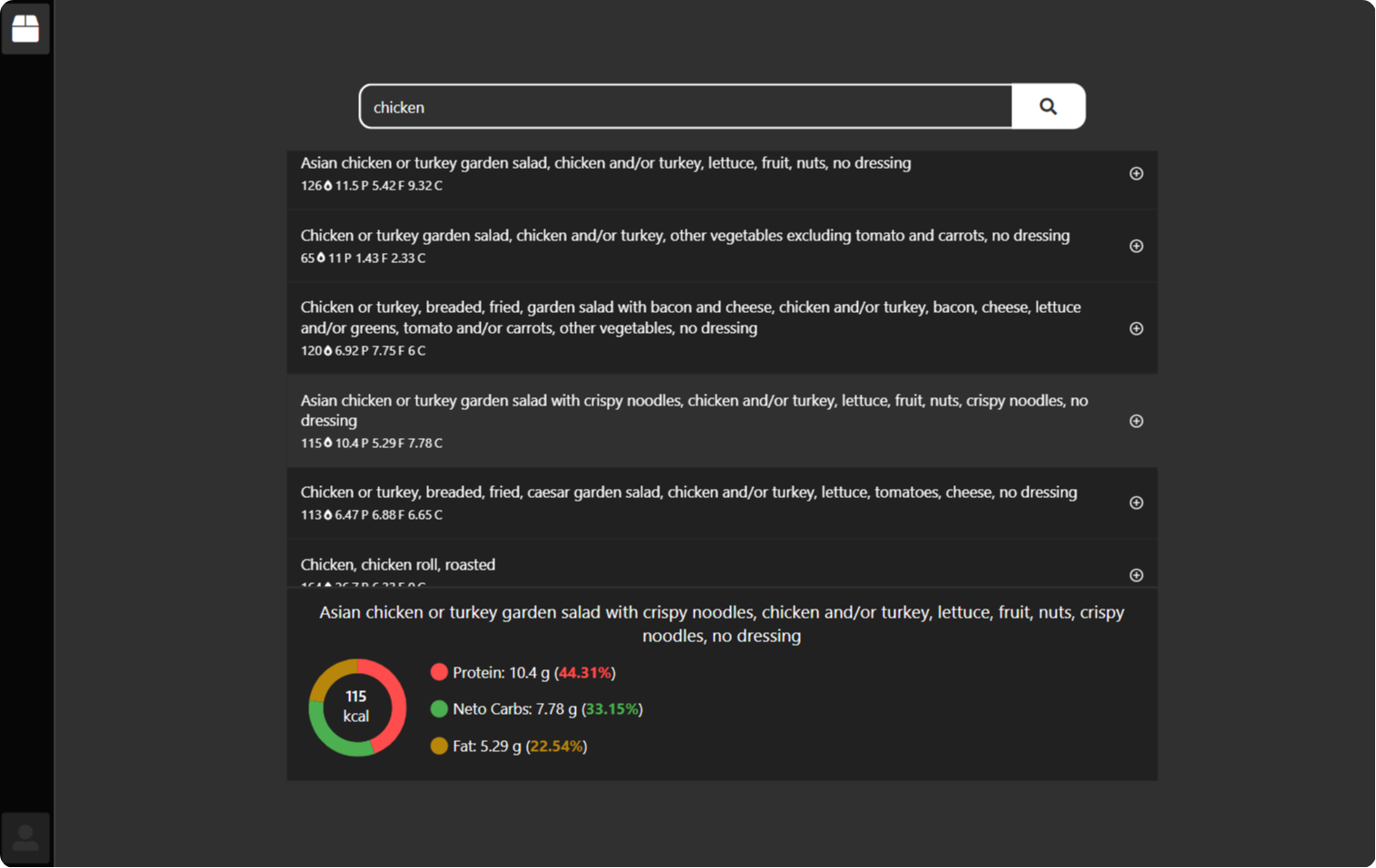
Free Macro Tracking App for Easy and Visual Nutrition Management
Track your macros, collaborate on meal planning, and get personalized insights with just one click. Enjoy unlimited food entries, meal plans, and user access.
Get Started • It`s FREEHelp
Need help with NoirNourish? We're here to support you! If something isn't working as expected, reach out for quick assistance and troubleshooting
Roadmap
Exciting updates are on the way! We're continually working to bring new features and improvements to NoirNourish to enhance your experience!
Community
Stay connected with the NoirNourish community on Instagram! Follow us for updates, tips, and inspiration, and join the conversation to make the most out of your wellness journey with us.
Follow us on Instagram
Achieve your dietary goals with NoirNourish
Join our community and take control of your nutrition with confidence using NoirNourish. Sign up today to access your personalized macro plan and food logging features, designed to support your wellness journey.
Start Now